Generates Two Different Yet Mathematically Related Keys
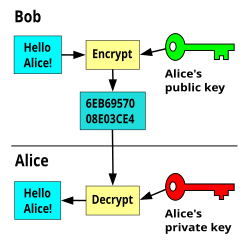
Unlike symmetric cryptography, public key cryptography uses two different keys - one public and one private. /corel-paintshop-pro-2019-key-generator.html. The keys are mathematically related, yet it is computationally infeasible to deduce one from the other. Anyone with the public key can encrypt a message but not decrypt it.
- Generates Two Different Yet Mathematically Related Keys In Word
- Generates Two Different Yet Mathematically Related Keys In Spanish
- Generates Two Different Yet Mathematically Related Keys 2017

Unlike symmetric cryptography, public key cryptography uses two different keys - one public and one private. The keys are mathematically related, yet it is computationally infeasible to deduce one from the other. Anyone with the public key can encrypt a message but not decrypt it. Asymmetric encryption involves two distinct — yet mathematically related — keys. Flash animation download mac free. One of those keys is called a public key and the other is called a private key. The public key, as the name implies, is publicly available and is used to encrypt the data. The private key, on. Involves using two mathematically related keys to perform the encryption and the decryption process. The exact mathematics of the encryption differ depending on the algorithm used, but in principle, this is how it works. An algorithm is used to generate a pair of keys that are related mathematically. Generates two different yet mathematically related keys. Asymmetric Only the private key can be used to decrypt information. Asymmetric Generates a single key that is used for both encryption and decryption. Symmetric Algorithm used for signature verification and data integrity checking. Hashing The public key can only be used to encrypt information.
public key algorithm
Generates Two Different Yet Mathematically Related Keys In Word
- خوارزمية المفتاح العموميAn asymmetric cipher that uses two keys, one for encryption, the public key, and the other for decryption, the private key. As implied by the key names, the public key used to encode plaintext can be made available to anyone. However, the private key must remain secret. Only the private key can decrypt the ciphertext. The public key algorithm used in this process is slow (on the order of 1,000 times slower than symmetric algorithms), and is typically used to encrypt session keys or digitally sign a message.
Generates Two Different Yet Mathematically Related Keys In Spanish
 Automatic translation:
Automatic translation: