Openssl Generate Self Signed Certificate And Key
Apr 12, 2020 With openssl self signed certificate you can generate private key with and without passphrase. If you use any type of encryption while creating private key then you will have to provide passphrase every time you try to access private key. Generating a private key and self-signed certificate can be accomplished in a few simple steps using OpenSSL. We provide here detailed instructions on how to create a private key and self-signed certificate valid for 365 days. Create the SSL Certificate. Now that we know the basics, let’s see how we can create a self-signed TLS/SSL certificate and configure it within our Apache and/or Nginx servers. The first thing to do is to create a / etc / ssl / private / folder on the server, which we’ll use to store the SSL/TLS key files. Since the secrecy of this key is.
Use openssl to create self-signed certificates and CSRs
Self-signed certificates offer the same level of encryption as commercial certificates, but you can generate them yourself and for longer durations of validity. University IT often uses self-signed certificates on development and test servers.
However, web browsers will present end users with an untrusted certificate warning if you use a self-signed certificate, so you should use a commercial certificate for your public-facing websites.
How to create self-signed certificates
These instructions employ the use of openssl. The first step is to create a private key and then the certificate. Be sure to keep the key in a secure location.
The example below creates a certificate with a 10-year (3652 days) validity. Replace <hostname> with the actual name of your server.
At the command line, enter:
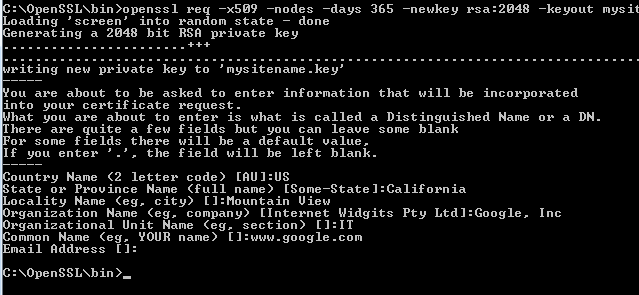
head /dev/urandom > /dev/nullopenssl genrsa -rand /dev/urandom -out <hostname>.key 2048openssl req -new -x509 -days 3652 -key <hostname>.key -out <hostname>.pem
The last command will require you to answer several questions before creating <hostname>.pem.
Country Name (2 letter code) []: US
State or Province Name (full name) []: California
Locality Name (e.g., city) []: Stanford
Organization Name (e.g., company) []: Stanford University
Organizational Unit Name (e.g., section) []: University IT
Common Name (e.g., web.stanford.edu) []: example.stanford.edu
Email Address []:
You can typically leave the email address and challenge password fields blank.
How to create a key and a CSR
To create both the key and CSR with one command, enter the following:
head /dev/urandom > /dev/nullopenssl req -new -newkey rsa:2048 -rand /dev/urandom -nodes -keyout <hostname>.key -out <hostname>.csr
You will be prompted to enter the details for your certificate. For Common Name, use the fully qualified hostname of your server. Leave the passphrase and email address empty.
How to create a new CSR with existing private key and cert.
openssl x509 -x509toreq -in existing_cert.pem -out new_csr.csr -signkey private.key
This is the quickest way to renew an expiring cert.
If you are using an old version of openssl you should add the '-sha256' option to ensure that you use the SHA-256 hashing algorithm instead of the older and less secure SHA-1 hashing algorithm.
SSL certificates are cool. They will be used more and more. This tutorial should be used only on development and/or test environments!
For a production environment please use the already trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs).
This key & certificate will be used to sign other self signed certificates. That will be covered in another tutorial.
here's a video:
Generate the CA key
Openssl Generate Self Signed Certificate And Key Download
You'll be prompted to enter a password.
openssl genrsa -des3 -out myCA.key 2048
Generate the Certificate
openssl req -x509 -new -nodes -key myCA.key -sha256 -days 3650 -out myCA.pem
3650 means that it will be valid for 10 years. Yes!
You can optionally remove the password from the key. For development purposes it would most likely be OK.
Openssl Create Self Signed Certificate Keystore
Make a backup of the original key
Linux/Mac: cp myCA.key myCA.key.with_pwd
Windows: copy myCA.key myCA.key.with_pwd
Export the CA key without a password
This is useful so you don't have to keep track of the password and/or use a script to sign self-signed SSL certificates.
openssl rsa -in myCA.key.with_pwd -out myCA.key
Openssl Generate Self Signed Certificate And Key Certificate
Convert the CA certificate from .PEM to .CRT format
openssl x509 -outform der -in myCA.pem -out myCA.crt
You may get the following errors:
How to fix OpenSSL error unable to write random state.
To fix this use this in the command line.
Windows
set RANDFILE=.rnd
Linux/Mac
export RANDFILE=.rnd
Another OpenSSL WARNING: can't open config file: /apache24/conf/openssl.cnf
This is fixable by setting an ENV variable that points to this file. I have copied this from my current Apache installation.
If you don't have it download it from this gist: https://gist.github.com/lordspace/c2edd30b793e2ee32e5b751e8f977b41
Windows: set OPENSSL_CONF=openssl.cnf
Openssl Generate Self Signed Cert
Linux: export OPENSSL_CONF=openssl.cnf
Openssl Generate Self Signed Certificate And Key With Passphrase
Related